Getting started with Nuxt Server Handlers
This post describes what Nuxt’s Server Handlers are and how to use them to create a todo application using the Xata serverless database platform.
Demola Malomo
Jan 03 2024
8 min read

Nuxt, Next.js, SvelteKit, and others consistently innovate their solutions based on the server-side rendering paradigm. This paradigm generates web content on the server side for each request, leading to improved web application performance, SEO, and user experience.
Beyond simply outputting and generating content on the web page, a notable addition in the Nuxt release is the support for Server Handlers. This feature enables us to define functions that run securely on the server and can return JSON data, a promise, or use event.node.res.end() as a response. The corresponding APIs can be called from Nuxt pages and components.
In this post, we will learn how to use Nuxt’s Server Handlers to create a basic todo application using the Xata serverless database platform. The project repository can be found here.
Prerequisites
To follow along in this tutorial, the following are required:
Project setup
In this project, we'll use a prebuilt UI to expedite development. To get started, let’s clone the project by navigating to a desired directory and running the command below:
1git clone https://github.com/Mr-Malomz/server-handlers.git && cd server-handlers
Running the project
Next, we’ll need to install the project dependencies by running the command below:
1npm i
Then, run the application:
1npm run dev

Setup the database on Xata
To get started, log into the Xata workspace and create a todo database. Inside the todo database, create a Todo table and add a description column of type String.

Get the Database URL and set up the API Key
To securely connect to the database, Xata provides a unique and secure URL for accessing it. To get the database URL, click the Get code snippet button and copy the URL. Then click the API Key link, add a new key, save and copy the API key.



Setup environment variable
To do this, update the nuxt.config.ts file to define a runtime configuration the application will use to load environment variables.
1// https://nuxt.com/docs/api/configuration/nuxt-config 2export default defineNuxtConfig({ 3 devtools: { enabled: true }, 4 css: ['~/assets/css/main.css'], 5 postcss: { 6 plugins: { 7 tailwindcss: {}, 8 autoprefixer: {}, 9 }, 10 }, 11 12 //add below 13 runtimeConfig: { 14 public: { 15 xataApiKey: '', 16 xataDatabaseUrl: '', 17 }, 18 }, 19});
Next, we must create an index.d.ts file in the root directory to type our runtime configuration.
1declare module 'nuxt/schema' { 2 interface PublicRuntimeConfig { 3 xataDatabaseUrl: string; 4 xataApiKey: string; 5 } 6} 7export {};
Finally, we must add our database URL and API key as an environment variable. To do this, create .env file in the root directory and add the copied URL and API key.
1XATA_DATABASE_URL= <REPLACE WITH THE COPIED DATABASE URL> 2XATA_API_KEY=<REPLACE WITH THE COPIED API KEY>
Integrate Xata with Nuxt
To seamlessly integrate Xata with Nuxt, Xata provides a CLI to install the required dependency and generate a fully type-safe API client. To do this, we need to run the command below:
1xata init
On running the command, we’ll have to answer a few questions. Answer them as shown below:
1Generate code and types from your Xata database <TypeScript> 2Choose the output path for the generated code lib/xata.ts
With that, we should see a lib/xata.ts file in the root directory.
A best practice is not to modify the generated code but to create a helper function to use it. To do this, create a utils/xataClient.ts file in the root directory and insert the snippet below:
1import { XataClient } from '~/lib/xata'; 2 3export const xataClient = () => { 4 const config = useRuntimeConfig(); 5 6 const xata = new XataClient({ 7 databaseURL: config.public.xataDatabaseUrl, 8 apiKey: config.public.xataApiKey, 9 branch: 'main', 10 }); 11 return xata; 12}; 13 14export interface ApiResponse<T> { 15 status: number; 16 message: string; 17 data?: T; 18 error?: { 19 message: string; 20 }; 21}
The snippet above imports the XataClient class from the generated code and configures the client with the required parameters. In addition, we also define an ApiResponse interface to describe our authentication response type.
Building the todo application
When a new Nuxt project is created, it includes a server directory. This directory is meant for registering Server Handlers for our application. The process involves creating directories and files inside the server directory. Nuxt will automatically scan and register these files and directories as Server Handlers with support for Hot Module Replacement.
1 -| server/ 2 ---| api/ 3 -----| hello.ts # /api/hello 4 ---| routes/ 5 -----| bonjour.ts # /bonjour
In our todo applications, we will use Server Handlers to do the following:
- Create a todo
- Get a todo
- Update a todo
- Delete a todo
- List todos
Create a todo
To create a todo, we need to create an api/createTodo.ts inside the server folder and insert the snippet below:
1import { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 2import { ApiResponse, xataClient } from '~/utils/xataClient'; 3 4export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => { 5 const xata = xataClient(); 6 const { description } = await readBody(event); 7 8 const response = await xata.db.Todo.create({ description }); 9 10 if (response.description) { 11 const successResponse: ApiResponse<TodoRecord> = { 12 status: 201, 13 message: 'success', 14 data: response, 15 }; 16 return successResponse; 17 } else { 18 const failureResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 19 status: 500, 20 message: 'failed', 21 error: { 22 message: 'Error creating todo', 23 }, 24 }; 25 return failureResponse; 26 } 27});
The snippet above does the following:
- Imports the required dependencies
- Creates a handler that extracts the required information and uses the
xataClientto create a todo. The function also uses theApiResponseinterface to return the appropriate response
Get a todo
To get a todo, we need to create a dynamic route api/[id].ts file and insert the snippet below:
1import { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 2import { ApiResponse, xataClient } from '~/utils/xataClient'; 3 4export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => { 5 const xata = xataClient(); 6 const id = event.context.params!.id; 7 8 if (!id) { 9 const emptyDescriptionResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 10 status: 400, 11 message: 'failed', 12 error: { 13 message: 'No id provided.', 14 }, 15 }; 16 return emptyDescriptionResponse; 17 } 18 19 const response = await xata.db.Todo.read(id); 20 21 if (response) { 22 const successResponse: ApiResponse<TodoRecord> = { 23 status: 200, 24 message: 'success', 25 data: response, 26 }; 27 return successResponse; 28 } else { 29 const failureResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 30 status: 500, 31 message: 'failed', 32 error: { 33 message: 'Error getting todo', 34 }, 35 }; 36 return failureResponse; 37 } 38});
The snippet above retrieves the dynamic parameter, checks if it is available, uses it to get the details of the associated todo, and returns the appropriate response.
Update a todo
To update a todo, we need to create an api/updateTodo.ts file and insert the snippet below:
1import { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 2import { ApiResponse, xataClient } from '~/utils/xataClient'; 3 4export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => { 5 const xata = xataClient(); 6 const { description, id } = await readBody(event); 7 8 const response = await xata.db.Todo.update(id, { description }); 9 10 if (response) { 11 const successResponse: ApiResponse<TodoRecord> = { 12 status: 200, 13 message: 'success', 14 data: response, 15 }; 16 return successResponse; 17 } else { 18 const failureResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 19 status: 500, 20 message: 'failed', 21 error: { 22 message: 'Error updating todo', 23 }, 24 }; 25 return failureResponse; 26 } 27});
The snippet above performs an action similar to the create todo functionality but updates the todo by searching for the corresponding todo and updating it.
Delete a todo
To delete a todo, we need to create an api/deleteTodo.ts file and insert the snippet below:
1import { ApiResponse, xataClient } from '~/utils/xataClient'; 2 3export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => { 4 const xata = xataClient(); 5 const { id } = await readBody(event); 6 7 const response = await xata.db.Todo.delete(id); 8 9 if (response) { 10 const successResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 11 status: 200, 12 message: 'success', 13 data: 'Todo deleted successfully', 14 }; 15 return successResponse; 16 } else { 17 const failureResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 18 status: 500, 19 message: 'failed', 20 error: { 21 message: 'Error deleting todo', 22 }, 23 }; 24 return failureResponse; 25 } 26});
The snippet above gets the id of a todo and uses the xataClient to delete the matching todo.
List todos
To get the list of todos, we need to create an api/listTodo.ts file and insert the snippet below:
1import { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 2import { ApiResponse, xataClient } from '~/utils/xataClient'; 3 4export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => { 5 const xata = xataClient(); 6 7 const response = await xata.db.Todo.getAll(); 8 9 if (response) { 10 const successResponse: ApiResponse<TodoRecord[]> = { 11 status: 200, 12 message: 'success', 13 data: response, 14 }; 15 return successResponse; 16 } else { 17 const failureResponse: ApiResponse<string> = { 18 status: 500, 19 message: 'failed', 20 error: { 21 message: 'Error getting todo list', 22 }, 23 }; 24 return failureResponse; 25 } 26});
The snippet above uses the xataClient to get the list of todos and returns the appropriate responses.
Putting it all together!
With that done, we can start using the handlers in the UI.
Update the create todo component
To do this, we need to modify the components/TodoForm.vue file as shown below:
1<script setup lang="ts"> 2const description = ref<string>(""); 3const errorMsg = ref<string>(""); 4const emit = defineEmits(); 5 6const onSubmit = async () => { 7 const response = await $fetch("/api/createTodo", { 8 method: "POST", 9 body: { description: description.value } 10 }) 11 if (response.status === 201) { 12 emit("todo-created", response.data); 13 description.value = ""; 14 errorMsg.value = ""; 15 } else { 16 errorMsg.value = String(response.error?.message) 17 } 18} 19</script> 20 21<template> 22 <form @submit.prevent="onSubmit"> 23 <p class="text-sm text-red-500 text-center" v-if="errorMsg !== ''">{{ errorMsg }}</p> 24 <textarea name="description" cols={30} rows={2} class="w-full border rounded-lg mb-2 p-4" 25 placeholder="Input todo details" required v-model="description" /> 26 <div class="flex justify-end"> 27 <div> 28 <button class="py-1 px-4 w-full h-10 rounded-lg text-white bg-zinc-800 hover:bg-zinc-900">Create</button> 29 </div> 30 </div> 31 </form> 32</template>
The snippet above utilizes the createTodo Server Handler by accessing it through the /api/createTodo route to create a todo.
Update the edit todo component
To update a todo, first, we need to modify the components/EditTodoForm.vue file as shown below:
1<script setup lang="ts"> 2import type { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 3 4const props = defineProps<{ 5 todo: TodoRecord 6}>(); 7const description = ref<string>(""); 8const errorMsg = ref<string>(""); 9 10watchEffect(() => { 11 if (props.todo) { 12 description.value = props.todo.description || ""; 13 } 14}); 15 16const onSubmit = async () => { 17 const response = await $fetch("/api/updateTodo", { 18 method: "PUT", 19 body: { id: props.todo.id, description: description.value } 20 }) 21 if (response.status === 200) { 22 description.value = ""; 23 errorMsg.value = ""; 24 await navigateTo('/') 25 } else { 26 errorMsg.value = String(response.error?.message) 27 } 28} 29</script> 30 31<template> 32 <form @submit.prevent="onSubmit"> 33 <p class="text-sm text-red-500 text-center" v-if="errorMsg !== ''">{{ errorMsg }}</p> 34 <textarea name="description" cols={30} rows={2} className="w-full border rounded-lg mb-2 p-4" 35 placeholder="Input todo details" required v-model="description" /> 36 <div className="flex justify-end"> 37 <div> 38 <button class="py-1 px-4 w-full h-10 rounded-lg text-white bg-zinc-800 hover:bg-zinc-900">Update</button> 39 </div> 40 </div> 41 </form> 42</template>
The snippet above does the following:
- Imports the required dependency
- Modify the component to accept a
todoprop - Creates an onSubmit function that uses the
updateTodoServer Handler by accessing it through the/api/updateTodoroute to update a todo
Lastly, we must modify the pages/[todo]/[id].vue file to get the value of a matching todo and pass in the required prop to the EditTodoForm component.
1<script setup lang="ts"> 2import { X } from 'lucide-vue-next'; 3import type { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 4 5const route = useRoute(); 6const todo = ref<TodoRecord>(); 7const errorMsg = ref<string>(""); 8 9const fetchData = async () => { 10 try { 11 const response = await $fetch<ApiResponse<TodoRecord>>(`/api/${route.params.id}`, { 12 method: "GET", 13 }); 14 if (response.status === 200) { 15 todo.value = response.data; 16 } else { 17 errorMsg.value = response.error!.message; 18 } 19 } catch (error) { 20 errorMsg.value = "Error fetching data"; 21 } 22}; 23 24onMounted(() => { 25 fetchData(); 26}); 27</script> 28 29<template> 30 <div class="relative z-10"> 31 <div class="fixed inset-0 bg-gray-500 bg-opacity-75 transition-opacity"></div> 32 <div class="fixed inset-0 z-10 w-screen overflow-y-auto"> 33 <div class="flex min-h-full items-end justify-center p-4 text-center sm:items-center sm:p-0"> 34 <div 35 class="relative transform overflow-hidden rounded-lg bg-white text-left shadow-xl transition-all sm:my-8 sm:w-full sm:max-w-lg"> 36 <div class="bg-white px-4 pb-4 pt-5 sm:p-6 sm:pb-4"> 37 <NuxtLink to="/" class="flex justify-end mb-2"> 38 <X class="cursor-pointer" /> 39 </NuxtLink> 40 <edit-todo-form :todo="todo!" /> 41 </div> 42 </div> 43 </div> 44 </div> 45 </div> 46</template>
Update the homepage to get the list of todos and delete a todo
To do this, we first need to modify the components/TodoComp.vue file as shown below:
1<script setup lang="ts"> 2import { Pencil, Trash2 } from 'lucide-vue-next'; 3import type { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; //add 4 5const router = useRouter() 6const props = defineProps<{ 7 todos: TodoRecord[] 8}>(); 9const errorMsg = ref<string>(""); 10 11const onDelete = async (id: string) => { 12 const response = await $fetch("/api/deleteTodo", { 13 method: "DELETE", 14 body: { id } 15 }) 16 if (response.status === 200) { 17 router.go(0) 18 } else { 19 errorMsg.value = String(response.error?.message) 20 } 21} 22</script> 23 24<template> 25 <div class='flex border p-2 rounded-lg mb-2' v-for="todo in props.todos" :key="todo.id"> 26 <div class='ml-4'> 27 <header class='flex items-center mb-2'> 28 <h5 class='font-medium'>Todo item {{ todo.id }}</h5> 29 <p class='mx-1 font-light'>|</p> 30 <p class='text-sm'>{{ todo.xata.createdAt.toString().slice(0, 10) }}</p> 31 </header> 32 <p class='text-sm text-zinc-500 mb-2'> 33 {{ todo.description }} 34 </p> 35 <div class='flex gap-4 items-center'> 36 <NuxtLink :to="`todo/${todo.id}`" class='flex items-center border py-1 px-2 rounded-lg hover:bg-zinc-300'> 37 <Pencil class='h-4 w-4' /> 38 <p class='ml-2 text-sm'>Edit</p> 39 </NuxtLink> 40 <button @click="onDelete(todo.id)" class='flex items-center border py-1 px-2 rounded-lg hover:bg-red-300'> 41 <Trash2 class='h-4 w-4' /> 42 <p class='ml-2 text-sm'> 43 Delete 44 </p> 45 </button> 46 </div> 47 </div> 48 </div> 49</template>
The snippet above does the following:
- Imports the required dependency
- Modify the component to accept a
todosprop - Creates an
onDeletefunction that uses thedeleteTodoServer Handler by accessing it through the/api/deleteTodoroute to delete a todo - Uses the prop to loop and display the required information
Lastly, we need to update the pages/index.vue file as shown below:
1<script setup lang="ts"> 2import type { TodoRecord } from '~/lib/xata'; 3 4const todos = ref<TodoRecord[]>([]); 5const errorMsg = ref<string>(""); 6 7const fetchData = async () => { 8 try { 9 const response = await $fetch<ApiResponse<TodoRecord[]>>("/api/listTodo", { 10 method: "GET", 11 }); 12 if (response.status === 200) { 13 todos.value = response.data!; 14 } else { 15 errorMsg.value = response.error!.message; 16 } 17 } catch (error) { 18 errorMsg.value = "Error fetching data"; 19 } 20}; 21 22const handleTodoCreated = (createdTodo: TodoRecord) => { 23 todos.value.push(createdTodo); 24}; 25 26onMounted(() => { 27 fetchData(); 28}); 29</script> 30 31<template> 32 <main class="min-h-screen w-full bg-[#fafafa]"> 33 <nav-bar /> 34 <div class="w-full mt-6 flex justify-center"> 35 <div class="w-full lg:w-1/2"> 36 <todo-form @todo-created="handleTodoCreated" /> 37 <section class="border-t border-t-zinc-200 mt-6 px-2 py-4"> 38 <p class="text-sm text-red-500 text-center" v-if="errorMsg !== ''">{{ errorMsg }}</p> 39 <p className='text-sm text-zinc-500 text-center' v-else-if="todos.length === 0">No todos yet!</p> 40 <todo-comp v-else :todos="todos" /> 41 </section> 42 </div> 43 </div> 44 </main> 45</template>
The snippet above gets the list of todos and passes in the required props to the components.
With that done, we can test our application by running the following command:
1npm run dev
Check out the demo below:
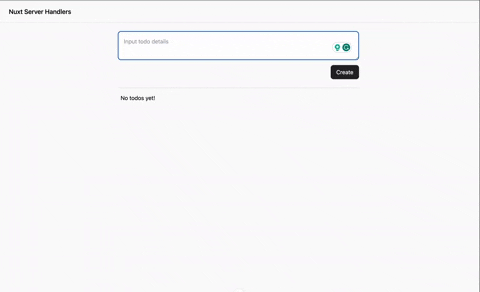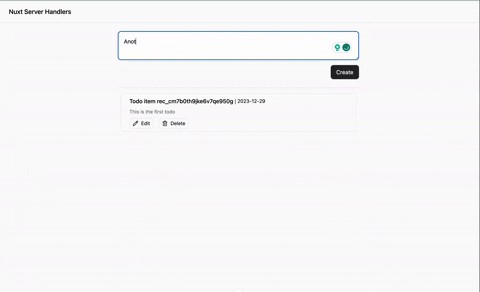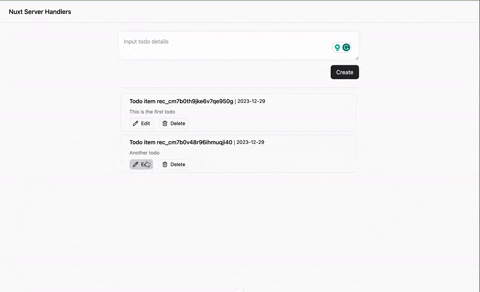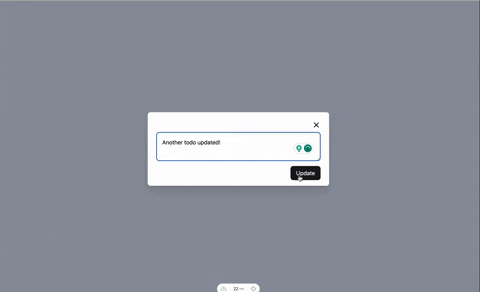
Conclusion
This post discusses how to use Nuxt Server Handlers to create a basic todo application. The server directory allows users to create APIs that run securely on the server.
Check out these resources to learn more:


